
Despite initial skepticism the evidence demonstrate the usefulness of the Apple Watch for the diagnosis of heart disease, and in the case that we are telling you today, it may have prevented a myocardial infarction and perhaps saved a life.
The case has been published in the magazine European Heart Journal, from the European Society of Cardiology, and tells us how an 80-year-old woman She was diagnosed with angina pectoris and treated for this pathology thanks to her Apple Watch, thus avoiding possible complications as serious as myocardial infarction (heart attack) and probably death for this reason. How did the Apple Watch achieve this diagnosis? Thanks to the ECGs that the woman performed at home and taught the doctors who treated her in the emergency room.
In the emergency room they found nothing abnormal
The 80-year-old woman, a German national, had a significant history of heart disease, such as high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, and pulmonary thromboembolism. The patient came to the emergency room with symptoms of chest pain, dizziness and palpitations (extrasystoles). In the emergency department, a complete electrocardiogram (12 leads) was performed, which at that time was normal. Troponin, a marker that rises in myocardial infarction, was also normal.
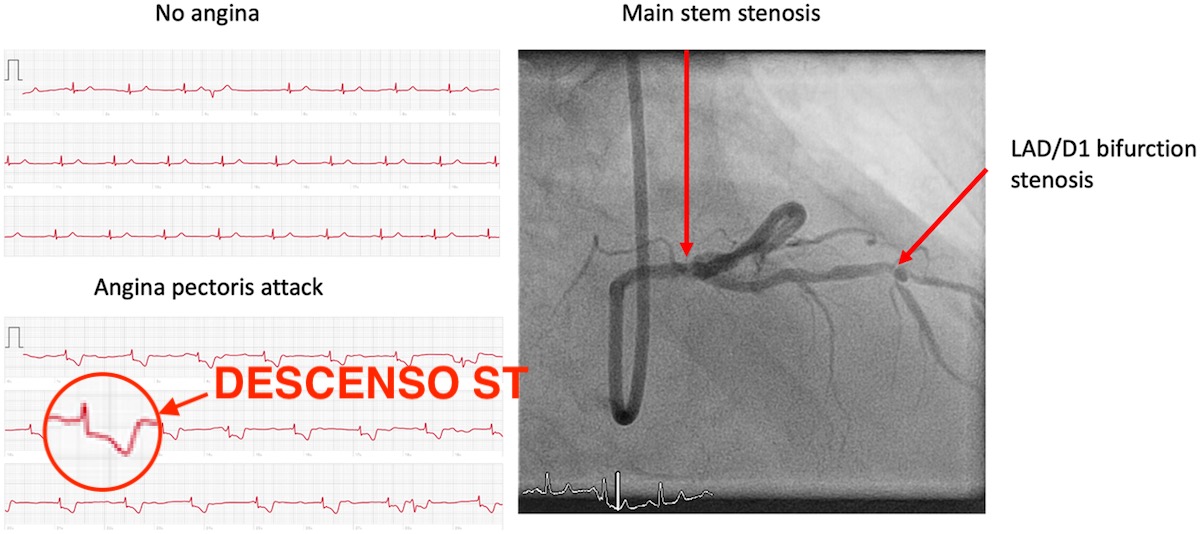
However, the patient showed the doctors the ECG that was performed at home while she had these symptoms thanks to her Apple Watch, and in them the doctors did find a very characteristic sign of angina pectoris: ST segment descent. Thanks to this study carried out by the Apple Watch, the woman immediately underwent arterial catheterization in which two lesions were evidenced in his coronary arteries, causing the symptoms for which he went to the emergency room.
How could that happen?
How can it be that he did not detect angina in the hospital? Angina pectoris occurs when one of the coronary arteries narrows and does not let enough blood flow to the heart. Its duration depends on whether there is damage to the heart or not. If there is damage, it is detected with the ECG and with the Troponin in blood, but if there is no damage because it has been short, it can be undetectable in both tests. That is why it does appear on the Apple Watch ECG (the patient had symptoms) and it does not appear on the hospital ECG (the crisis had already subsided).
The Apple Watch ECG is very limited by having only one lead (a medical ECG has 12 leads), in fact Apple makes it very clear that "it is not a useful device to detect myocardial infarction", since it cannot detect any heart attack that may occur, but in this case it did detect it and it was also extremely useful. Having an ECG always available on your wrist allows you to use it in case of any symptoms, which in heart disease is really important, since many are transitory and have disappeared when you arrive at the hospital.
To have if they activate the option here in Australia, since they have it, and the truth when I found out about it I was disappointed I tried to change it in Spain but nothing